
What are non-manufacturing costs or period costs?
For example, a small business that manufactures widgets may have fixed monthly costs of $800 for its building and $100 for equipment maintenance. These expenses stay the same regardless of the level of production, so per-item costs are reduced if the business makes more widgets. Cost of goods sold is usually the largest expense on the income statement of a company selling products or goods. Cost of Goods Sold is a general ledger account under the perpetual inventory system. Note 1.43 “Business in Action 1.5” details the materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead at a company that has been producing boats since 1968.
Direct Manufacturing Overhead Costs
This account balance or this calculated amount will be matched with the sales amount on the income statement. It is likely that you will have to estimate the cost of these activities. Next, you will need to allocate the cost of the activities to the individual products. Estimates and allocations based on logical assumptions are better than precise amounts based on faulty assumptions.
What are Nonmanufacturing Overhead Costs?
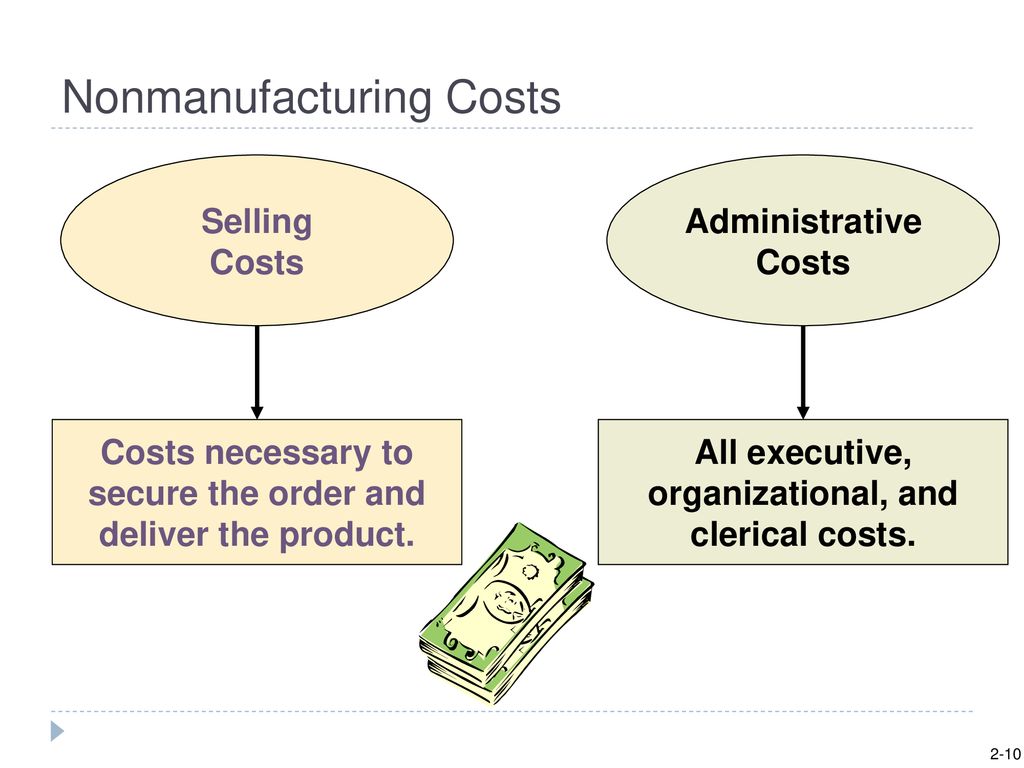
Executive salaries, clerical salaries, office expenses, office rent, donations, research and development costs, and legal costs are administrative costs. Since nonmanufacturing overhead costs are outside of the manufacturing function, these nonmanufacturing costs are immediately expensed in the accounting period in which they are incurred. That is why accountants refer to nonmanufacturing costs as period costs or period expenses. Although selling costs and general and administrative costs are considered nonmanufacturing costs, managers often want to assign some of these costs to products for decision-making purposes. For example, sales commissions and shipping costs for a specific product could be assigned to the product.
Examples of Nonmanufacturing Overhead Costs
Indirect labor (part of manufacturing overhead) includes the production supervisors who oversee production for several different boats and product lines. In summary, product costs (direct materials, direct labor and overhead) are not expensed until the item is sold when the product costs are recorded as cost of goods sold. Period costs are selling and administrative expenses, not related to creating a product, that are shown in the income statement along with cost of goods sold. Direct labor manufacturing costs is determined by calculating the cost of employees directly responsible for producing the product. For example, a clothing manufacturer considers employees that dye the cloth, cut the cloth and sew the cloth into a garment as direct labor costs. However, designers and sales personnel are considered nonmanufacturing labor costs.
Manufacturing Overhead Outline
While this is a simplified view of direct labor calculation, accountants also include the benefits, overtime pay, training costs, and payroll taxes when calculating the hourly rate. To ensure that you understand how and why product costing is done in manufacturing companies, we use many manufacturing company examples. However, since many of you could have careers in service or merchandising companies, we also use nonmanufacturing examples. For a further discussion of nonmanufacturing costs, see Nonmanufacturing Overhead Costs.
Example #1: Direct materials
- While manufacturing or production costs are the core costs for a manufacturing entity, the other costs are also just as important as they too affect overall profitability.
- Manufacturing overhead includes the indirect materials and indirect labor mentioned previously.
- Note “Business in Action 2.3.2” provides examples of nonmanufacturing costs at PepsiCo, Inc.
Now, add the value of existing inventory to the cost of purchasing new inventory to calculate the cost of direct materials. Start by making a list of all the direct materials that are used to make the specific product and obtain the cost information for the direct materials you have identified. To calculate the cost of direct materials taxpayers have more time to file in 2017 you need to know the cost of inventory. According to a study conducted by McKinsey, these indirect costs account for 8% to 12% of the overall manufacturing costs. According to McKinsey’s research, cutting down manufacturing costs, in addition to boosting productivity, is the key for manufacturing companies to remain competitive.
Note “Business in Action 2.3.2” provides examples of nonmanufacturing costs at PepsiCo, Inc. Note 1.48 “Business in Action 1.6” provides examples of nonmanufacturing costs at PepsiCo, Inc. Material costs are the costs of raw materials used in manufacturing the product. By calculating manufacturing costs, manufacturers can better understand the elements that are driving up costs while identifying the most economical way to manufacture a product.
This helps them understand the most efficient process and the investment they need to make for the selected process. A manufacturing company initially purchased individual components from different vendors and assembled them in-house. As the company decided to assemble the components themselves, they found that the costs of managing the assembly line and the transportation were increasing significantly. According to the book Manufacturing Cost Estimating, the benefits of calculating the costs of manufacturing range from guiding investment decisions to cost control. The opportunity to achieve a lower per-item fixed cost motivates many businesses to continue expanding production up to total capacity. Cost is a financial measure of the resources used or given up to achieve a stated purpose.
To obtain these details, you can refer to the company’s employment records that has a list of all the employees and their hourly rates. For instance, let’s say a company has an existing inventory worth $1,500. A project cost overrun happens when the project costs exceed the budget estimate. That’s why you need a reliable partner to buddy up with and slash your costs.
Nonmanufacturing overhead costs are the company’s selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses plus the company’s interest expense. MasterCraft records these manufacturing costs as inventory on the balance sheet until the boats are sold, at which time the costs are transferred to cost of goods sold on the income statement. PepsiCo, Inc., produces more than 500 products under several different brand names, including Frito-Lay, Pepsi-Cola, Gatorade, Tropicana, and Quaker.

After subtracting the manufacturing cost of $10, each widget makes $90 for the business. Direct materials are those materials used only in making the product and are clearly and easily traceable to a particular product. For example, iron ore is a direct material to a steel company because the iron ore is clearly traceable to the finished product, steel. In turn, steel becomes a direct material to an automobile manufacturer.
